Recent Comments
Recent Posts
Archives
Categories
https://onedrive.live.com/embed?cid=290CB921F233A7CB&resid=290CB921F233A7CB%21781&authkey=AF8pVIMBleToklg&em=2
Solar Hot Water Systems by Trade Secrets
How to identify the most practical setup for a solar hot water system based on the needs of the climate, building, and the households.
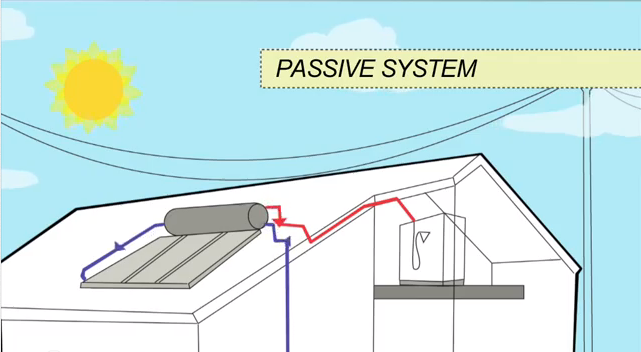
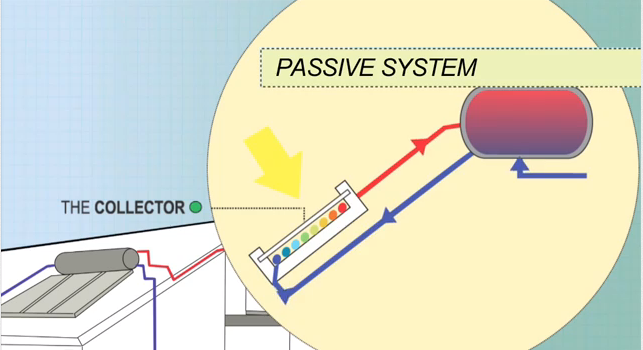
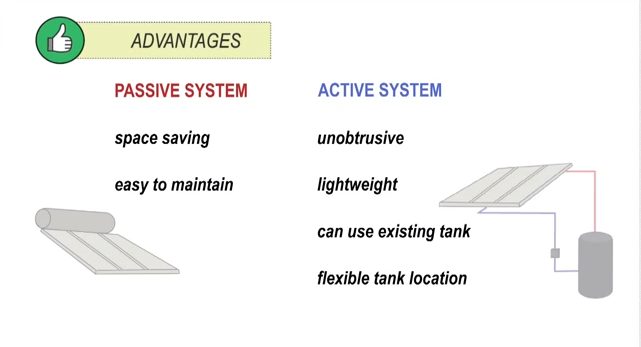
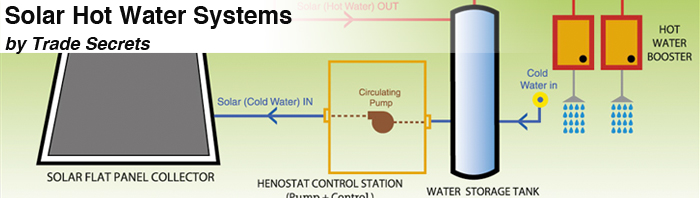
Passive System
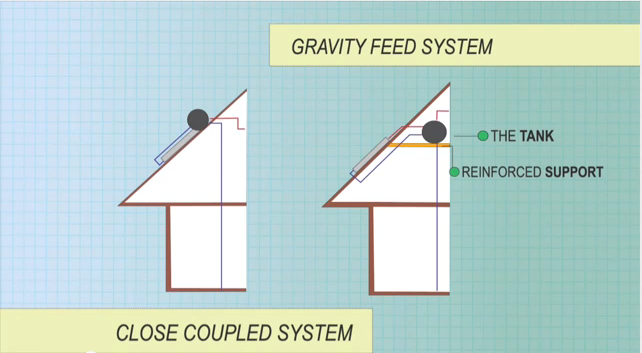
In passive system, also known as thermosiphon system, the tank sits above the collectors. Cold water sinks into the collectors, which warm water rises unassisted from the collectors into the tank. The tank might sits on top of the roof (Close Coupled System), or within the roof cavity above the collector (Gravity Feed System). With these systems, the roof’s support systems must be strong enough to handle up to 800 kilograms.
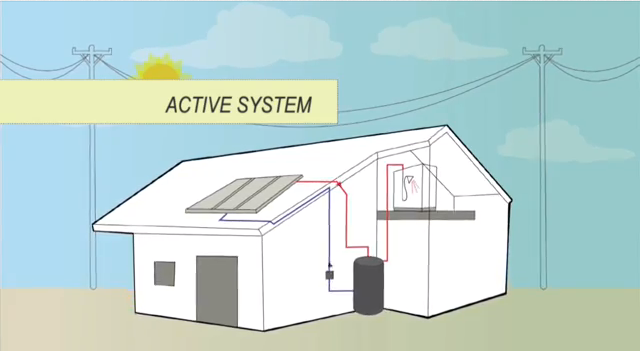
Active System
Active system uses a small pump to move water between collectors and the tank. The location of the tank can be within the roof or on the ground.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The Collectors
There are two types of collectors to choose from: flat plate and evacuated tubes.
Evacuated tubes have the advantage of receiving perpendicular radiation for greater part of the day. These combined with insulation illustrate good winter performance.
Flat Plates, usually purchased at par with close coupled system, can be more affordable than evacuated tubes collectors. However, the price for evacuated tubes have fallen in recent years.
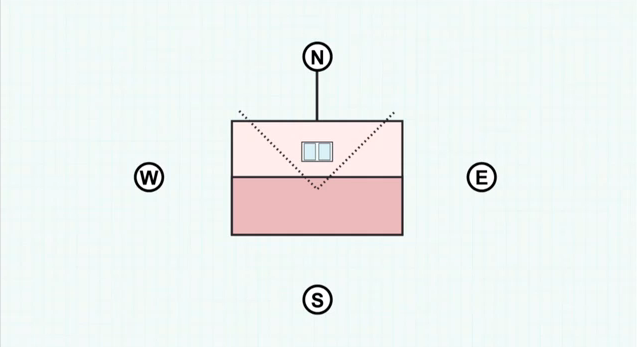
Collectors should ideally face north in a shade-free position. Facing the collectors 45 degrees from the true north will only result in minor reduction of performance.
The ideal inclination is the ange of latitude plus 5 to 10 degrees.
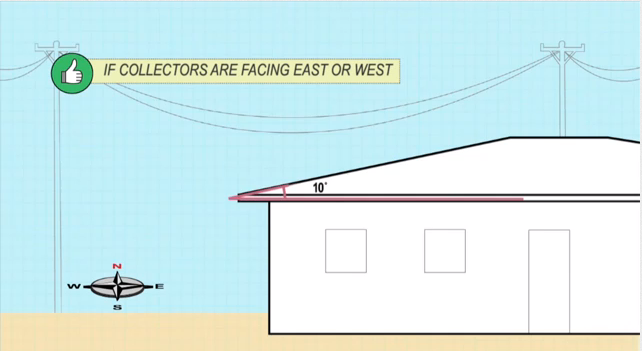
If collectors face East of West, the lower the angle of inclination, the better.
However, to ensure the thermosiphon flow, you must always keep the angle above 10 degrees.
For the correct sizing of your collectors and tank, insult manufacture guidelines to see what is the best for the climate and household.
Temperature Protection
In places with minor frosts, evacuated tubes may offer minor in-build protection.
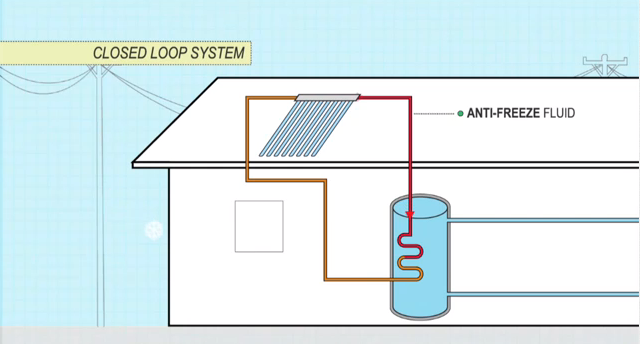
In climates with regular frosts, closed-loop system is the most reliable form of frost protection.
Instead of water, an anti-freeze fluid, instead of water, is hidden in the collectors.
Other frost protection methods are also available, such as frost protection valve, temperature controlled pumps, drainback system.
Boosting
The solar hot water system will require boosting at some time of the year. Electric booster use a lot of power, so make sure the booster is controlled by an in-house manual switch. Booster that have no manual switch, or are permanently on are wasteful as they often heat water to 60 degrees Celsius, water which otherwise be heated by the sun. When advising the household on the solar electric tariff system, examine the pros and cons of each options. The right tariff will minimize carbon emission and cost.